When going zero waste it can be very helpful to avoid plastics. Many others are also being considered that will replace plastic, including the Silicone. Besides durability and flexibility, these materials are able to resist extreme temperatures. How can we make silicones more environmentally-conscious?
Is silicone plastic or rubber?
Silicone is not plastic nor rubber in the conventional sense. This is a special polymer, manufactured from silicon, oxygen and carbon combined with hydrogen. It is, however, not as similar to rubber in fate and structure as many people think. Flexible and heat resistant silicone has its own molecular structure apart from that of natural materials such as wood or iron. Unlike the more commonly used rubber proteins, silicone is thought to be non-toxic and inert as well as highly resistant to extreme temperatures.

Silicone is not plastic nor rubber in the conventional sense. This is a special polymer, manufactured from silicon, oxygen and carbon combined with hydrogen. It is, however, not as similar to rubber in fate and structure as many people think. Flexible and heat resistant silicone has its own molecular structure apart from that of natural materials such as wood or iron. Unlike the more commonly used rubber proteins, silicone is thought to be non-toxic and inert as well as highly resistant to extreme temperatures.
Is silicone eco-friendly or as toxic as plastic?
Unlike plastic, silicone is seen as a much more environmentally friendly material. While many plastics are inferior to silicone in such respects as being durable, heat-resistant and recyclable. Because it comes from silica, a normal ingredient of sand, which is widespread and does not rely on fossil fuels for production. In addition, silicone products often last longer than other types leading to fewer replacements.
Additionally, silicone is considered inactive and not toxic. It has fewer environmental impact risks compared to some types of plastics which may contain harmful ingredients or else give off toxic substances during production or use. Though silicone does not pose the same threat to our environment as some plastics, its pro-environment image is afforded largely by its material structure and recyclability.
Silicone Isn’t Always Right for the Job
With so many good points in its favor, and such versatility potential itself, silicone is not necessarily the best solution for every application. As it has excellent heat resistance and strength, there are only some applications which require a material that possesses greater rigidity than Po. Moreover, silicone tends to be more expensive than other materials and that can affect decision in cost-conscious applications. There are exceptions, and its flexibility can be a disadvantage when rigid support is essential for engineering or construction.
Also, the silicone recycling system is not as well-developed an ecosystem like traditional plastics; this may negatively affect its long term environmental sustainability.
Therefore, in evaluating whether silicone is the best choice of material for a particular task it needs to be carefully considered what exactly each individual job requires and how much money can be spent as well as environmental aspects.
Is silicone biodegradable?

In general, silicone does not biodegrade naturally in the same way as organic materials. Its chemical structure is very stable, so it resists microbial and other forms of decomposition. This durability not only allows silicone to live a long life and withstand environmental pressures, but it also means that this does not easily undergo biodegradation.
Hence, silicone waste remains in the environment for a long time and is difficult to dispose of. Fragments may be harmful to ecological health.
Currently silicone is not considered to be a biodegradable material; however, efforts are being made to find more sustainable choices with regards both production and recycling.
Several key environmental advantages:
Some of the major environmental benefits are waste reduction, resource conservation and low ecological impact.
- Waste Reduction: Sustainable practices can also greatly reduce the rate of waste generation, making it far easier to recycle material and reducing environmental pollution.
- Resource Conservation: Eco-friendly technologies and practices will enable the conservation of scarce natural resources like water, energy and raw materials for constant environmental improvement.
- Resource Conservation: Eco-friendly technologies and practices will enable the conservation of scarce natural resources like water, energy and raw materials for constant environmental improvement.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: By adopting efficient energy use, sustainable transport and carbon offsets, one can greatly reduce the so-called carbon footprint. This reduces our encroachment on nature and global warming.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Preserving biodiversity includes efforts such as protecting natural habitats and encouraging appropriate land use.
- Circular Economy Principles: Circular economy-based production and consumption takes a more sustainable approach.
- Eco-friendly Materials: Making products out of biodegradable materials that are environmentally friendly reduces the environmental impact and provides support for a more responsible product life cycle.
- Environmental Education: Public education and awareness about sustainable practices encourages people and businesses to make informed choices, creating an environmental culture.
- Resilient Ecosystems: In protecting natural ecosystems and their biodiversity, therefore societies help to create a more resilient environment that is better able to endure ecological challenges.
- Mitigation of Pollution: Pollution can be reduced through sustainable practices like landfill waste management and reduction of emissions with harmful effects. This keeps air clean, water safe to drink, as well as the quality of soil high.
A smaller carbon footprint can be achieved through the use of recycling and renewable energy sources. Using environmentally friendly technologies and materials, such as energy-efficient appliances or biodegradable packaging can reduce environmental destruction. Conservation work, including protecting biodiversity and keeping ecosystems intact, keeps the planet balanced. Also on the basis of circular economy principles–in which resources are reused and regenerated in an effort to be environmentally sustainable over time. Combined, these advantages make human activity more environmentally responsible and resilient.
Silicone Vs Plastic: Which is safer?
Compared to plastic, generally speaking silicone is considered safer for some applications. Because silicone is inert it does not leach harmful chemicals into foods or liquids and thus has always been popular for use as kitchenware, baby products and medical implants.
It is more heat-resistant than many plastics, and stable under high temperatures without releasing toxins. On the other hand, some plastics contain additives–such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA)–which may have adverse effects on human health.
But it should be noted that any material is only as safe as its particular formulation and use. Despite silicone’s advantages of inertia and resistance to heat, factors such as recycling and environmental impact must also be considered when discussing whether it is better than or different from plastic.
How to choose food-safe silicone?
It’s especially important to select safe food silicone so that the material won’t leach harmful substances into your dishes. Here are some guidelines to help you select food-safe silicone products:

Check for Certification:
And be sure to choose products whose labels indicate that they are food-grade silicone or which have been certified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In your home country, look for FDA approval, LFGB compatibility or similar standards of food safety certification
Read Product Labels:
You should examine product labels to find out what type of silicone is used. Food-grade silicone must, of course be free from fillers and additives which would endanger its safety.
Odor and Taste Test:
Food-grade silicone, of good quality should not affect the taste or smell of your food. If you notice a strong or unpleasant smell, this may indicate contaminants.
Look for Reputable Brands:
Select products from familiar, reliable brands that stress safety and quality. For further information, see customer reviews and ratings.
Color Consideration:
For kitchenware, the more often seen is clear or translucent silicone that contains less chance of dyes and additives. The colored silicone should be marked foodsafe. And the coloring agents used must meet safety criteria too.
Temperature Resistance:
Be sure that the silicone product is made to withstand temperatures within your intended temperature range. Generally speaking, food-grade silicone is safe for use in ovens, microwaves and freezers.
Avoid Cheap or Unknown Brands:
Do not be tempted by excessively cheap silicone products with no brand name, as they may just ignore safety. With high standards for production and testing procedures, quality food-grade silicone doesn’t come cheap.
Flexibility and Texture:
Food-grade silicone should have a smooth feel and be flexible. If the material feels sticky, too soft or uneven in texture it may be product of lower quality.
Check for Wear and Tear:
Check the product for wear, discoloration or damage. If the silicone is damaged, its integrity may be compromised and harmful substances could escape.
Are There Any Silicone Alternatives?
Yes, there are substitutes for silicone according to the type of application and desired properties. Some common alternatives include:
Rubbery material
When flexibility and resilience are important, natural or synthetic rubber could be used. But perhaps rubber doesn’t resist temperatures like silicone does.
Plastics
The use case may call for different plastics–polyethylene, polypropylene or even polyurethane. It’s also important to select plastics that are free of harmful additives like BPA.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel serves as an alternative in the case of some kitchenware and cooking utensils. It is strong, easy to wash off and resistant to high temperatures.
Glass:
Glass
Glass is an inert material that does not leach harmful substances into food and beverages. It makes a fine substitute for food storage containers and cooking dishes.
Bamboo

Bamboo is a renewable, recyclable resource which can be substituted for silicone in some products such as kitchen implements (spoons and spatulas), cutting boards or plates.
Cotton and Linen
Silicone can be replaced by natural fabrics such as cotton and linen in some applications. For instance, pot holders and oven mitts can be fashioned from heat-resistant materials.
Wood
Cutting boards, bowls and wooden kitchen utensils provide alternatives to silicone for food preparation and serving.
Ceramics
Dishes, bowls and baking dishes: ceramic materials like porcelain or stoneware can be used. They are usually safe and do not leach harmful substances.
In evaluating possible substitutes, we must look carefully at the particular demands of actual use. Heat resistance or flexible? Should it be strong and sturdy or thin and pliant for easy handling? Moreover, one should also ensure that the alternative product is certified under such things as FDA approval or other safety standards prior to use. Remember each material has its own pluses and minuses. The best one is up to the needs of users, so choose wisely!
Can you recycle silicone?
Because silicone is a very hardy and stable substance, recycling it can be difficult. Silicone cannot be recycled by traditional methods, and does not easily break down in nature. But some companies and organizations are coming up with novel ways to reuse silicone. Similarly, many silicone recycling programs require that the material be broken down into its original components for reuse.
Silicone recycling is still less widespread and established than the recycling of everyday items like plastic or glass. Ongoing research, as well as developments in technology strive for increased sustainability and to reduce negative effects on the environment. Thus far, one must first contact local recycling programs or specialized plants that may take in silicone products for reuse.
Sourcing Silica for Silicone biodegradable
Silicone is usually made from silica, which itself consists of the elements silicon and oxygen. Sand is abundant in nature and provides the main source of silica. The process of extracting silica from sand is called silica sand mining, in which huge deposits (sands) rich with the mineral are harvested for such industrial uses as making silicone.

Part of the evaluation when considering environmental impact and sustainability is in looking at how silica sand was sourced. Here are some key considerations:
- Sustainable Mining Practices– Seek suppliers or manufacturers that practice sustainable mining. Thus, efforts at responsible land reclamation should both minimize the ecological impact of mining operations and conserve local ecosystem.
- Ethical Sourcing – Select suppliers who focus on ethically sourced silica. This means ensuring decent work, the right of local people to be involved in decision making and reducing environmentally harmful practices.
- Recycled Silica – There are also some planned efforts related to the use of reclaimed silica in making silicone. This entails recovering silica from post-consumer or post-industrial sources, thereby establishing a circular economy and reducing the pressure for new extraction.
- Certifications and Transparency – Look for products and manufacturers that either adhere to recognized standards or certifications related to responsible sourcing, sustainable production. The environmental and social impact of silica extraction can be assessed only if sufficient transparency exists in the supply chain.
- Alternative Sources – Check the possibility of switching to sources of silica with a lower environmental impact. Some firms are investigating and developing new ways to extract silica from agricultural wastes or other renewable sources.
Thus by adopting a less environmentally harmful model of sourcing silica, the environmental impact of producing silicone as well can be reduced. Remember that responsibility for environmental sustainability does not end at the time of sourcing raw materials; it includes the entire production process, recycling plans and silicone products’ after-life management details. Always contact manufacturers to ask about their sustainability practices, and choose those that stress environmental considerations.
Is silicone a hazardous waste?
Silicone alone, however, is not usually regarded as hazardous waste. It is a stable, inert material and its chemical composition presents no immediate health risk or environmental harm.

But the nature of silicone waste depends on what additives or impurities it contains and how it is discarded. Silicone waste could well be dangerous if contaminated or mixed with other materials.
Waste from silicone is easily managed, just so long as the method of disposal satisfies local regulations and guidelines for safety to people’s health. Since silicone is slow to biodegrade, proper waste disposal becomes very important for addressing its long-term impact on the environment.
What is silicone made out of?
Silicones are a group of man-made synthetic polymer containing silicon, oxygen, carbon and hydrogen. It is composed of silicon and oxygen with the chemical symbol SiO2, which has a common abbreviation as quartz. The manufacture of silicone is by no means a simple process. Before they’re even produced as polymers, natural resources first must be sacrificed in the chemical reaction known as the synthesis of silicon (or prenatal makeup).

That is the highly versatile polymer, unique in its combination of flexibility, heat resistance and low toxicity with high durability.
Different formulations and processes produce silicone products with various characteristics, making them suitable for many uses such as sealants, adhesives. medical implants, cookware etc.
Does silicone release toxins when heated?

For the most part, silicone is harmless for cooking or baking because it doesn’t release toxins when heated. High quality food-grade silicone, unlike some plastics that may contain harmful additives is both stable and inert at high temperatures.
That is to say when heated it does not decompose, and will not leach poisons into the food or environment.
Because silicone is resistant to heat, up to temperatures above and beyond those used in cooking, it’s often selected as a material for kitchen utensils, bakeware or other household implements.
Yet people must use silicone products in accordance with purpose and temperature guidelines to guarantee their safety.
What are examples of environmentally friendly products?
Eco-friendly or green products are those which cause the least impact on the environment from their birth to death. Examples include:

Reusable Water Bottles: Water bottles made from such materials as stainless steel or BPA-free plastics last longer than disposable ones, and can reduce the need for throwaway plastic water bottles.
Reusable Shopping Bags: Using cloth or recycled-material shopping bags helps reduce the usage of single-use plastic bags, reducing environmental pollution.
LED Light Bulbs: Unlike incandescent bulbs, energy-efficient LEDs use less electricity and last longer. Their low usage of electricity combined with their greater longevity can reduce waste sources.

Biodegradable Cleaning Products: But even so, cleaners with biodegradable ingredients are less harmful to the environment and decompose more easily than traditional chemical-based cleansers.
Bamboo Products: Bamboo is a fast-growing, renewable resource. Alternatives to plastic include bamboo utensils, toothbrushes and cutting boards.
Solar Chargers: Portable solar chargers use the energy of the sun to charge many kinds of electronic devices, providing an environmentally sound alternative to plug-in electrical chargers.
Organic Cotton Clothing: Clothing made using organic cotton is cultivated organically and also does not require harmful pesticides.

Compostable Cutlery and Plates: Cutlery and plates fashioned from such materials as cornstarch or sugarcane are compostable, which eliminates some of the ecological costs associated with throwaway eating utensils.
Electric or Hybrid Vehicles: Electric- and electric–conventional fuel-driven cars emit less greenhouse.
Eco-Friendly Packaging: By using packaging made from recycled materials or designed to be easily-recyclable, companies can reduce the environmental impact of product packaging.
Is Silicone Toxic to Humans?
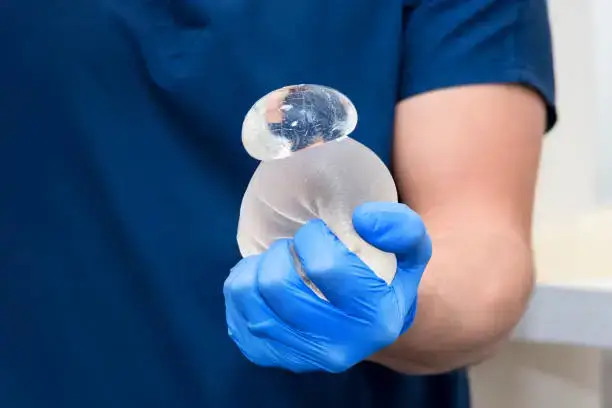
Silicone is generally thought to be harmless and nontoxic. Medical-grade silicone, as well as food-grade silicon are carefully tested to ensure their safety for use in medical implants, kitchenware or baby products. Because silicone is biocompatible (or well-tolerated by the human body), it doesn’t generally provoke an immune response.
Silicone is used in so many kitchen utensils, bakeware and food containers because it releases no harmful substances when heated. It is stable and inert, making it suitable for a great many culinary applications.
Is silicone durable?
Yes, silicone is supposed to be strong and long-lasting. A synthetic polymer which resists wear and tear very well, it is extremely versatile in use. Flexibility and Resilience: The moral structure of silicone gives it the ability to bend or stretch many times without losing its shape. What’s more, silicone is able to withstand extreme temperatures and UV rays as well as rough conditions in nature. All this explains why they are long-lived creatures. Because of this durability, silicone is a choice material for many products used in the kitchen or bakeware. It also finds applications in everything from medical devices to industrial equipment.
Should you use silicone products?
Due to their versatile and beneficent properties, the use of silicone products is generally recommended for a number of applications. Silicone is tough, flexible and heat-resistant, which explains its application in kitchenware as well as bakeware or medical devices.
High-quality silicone does not release harmful substances when heated and is therefore considered to be safe for cooking or food storage. However, silicone products should be used in the way they are intended and according to manufacturer’s instructions. Only high-quality, food-grade or medical grade silicone should be chosen for your safety and longevity. Silicone does have many advantages, though personal considerations such as cost and environmental impact may affect the choices people make when using products for particular purposes.
Because silicone products are tough, flexible and heat-resistant they are versatile in their usage just like silicone rubber, silicone oil, pure silicone, silicone recyclable especially in recycling silicone. Silicone, which is safe and inert, is recommended for a broad range of applications including kitchen utensils and even medical devices which is the silicone environmentally friendly which you can have silicone bakeware have synthetic material, the silicone menstrual cups were womens can use this also plastic pollution which belongs to plastic products and silicone manufacturers. It’s also suitable for cooking as well as food storage or food containers if you will go to the mall you can use silicone bags, which is good for recycle silicone products. It is important to select quality silicone products and follow recommended guidelines those can sustainable material, more eco friendly alternative and silicone safe. Although silicone has many advantages, decisions about its use rests on various considerations such as cost and environmental impact.